| RSGC ACES: TMP36 Monitoring and Logging (November 2025) |
Microcontrollers are ideal for the monitoring and logging of sensor data. This set of investigations provides you with a basic introduction to an approach to scheduling (Library: TimerOne.h ) the reading and recording (Library: EEPROM.h) of a simple temperature sensor (TMP36) with your Arduino Nano.
| TMP36 Temperature Sensor | From the Adafruit Blog |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Investigations
1. Scheduled Sampling of the TMP36 Temperature Sensor
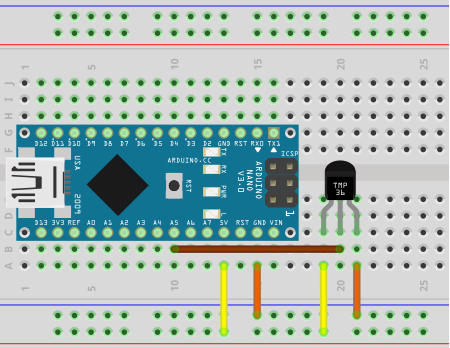 The TMP36 in your kit comes in the same TO-92 package as your 2N3904 and 2N3906 BJT transistors. The general description from the datasheet conveys the following,
The TMP36 in your kit comes in the same TO-92 package as your 2N3904 and 2N3906 BJT transistors. The general description from the datasheet conveys the following,
"The TMP35/TMP36/TMP37 are low voltage, precision centi-
grade temperature sensors. They provide a voltage output that
is linearly proportional to the Celsius (centigrade) temperature.
The TMP35/ TMP36/TMP37 do not require any external
calibration to provide typical accuracies of ±1°C at +25°C
and ±2°C over the −40°C to +125°C temperature range."
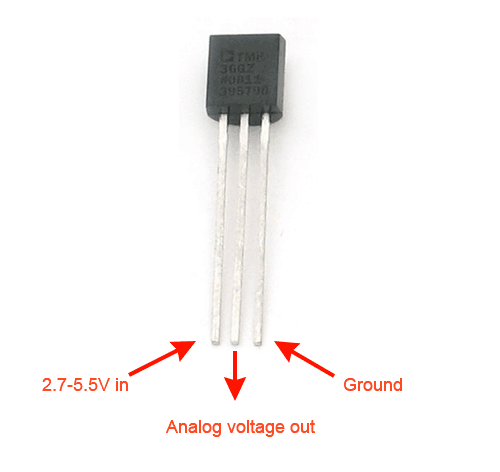
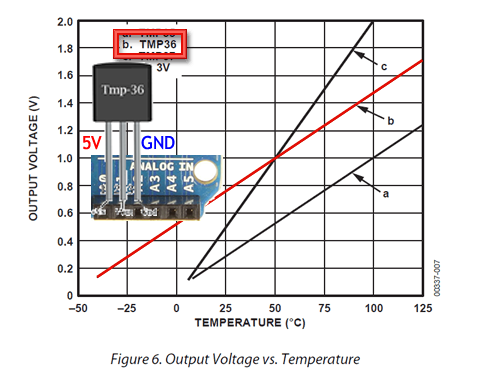
From this we determine that your Nano's analogRead() function can capture a 10-bit reading from Pin 2 of the TMP36 before linearly scaling it to a Celsius (centigrade) temperature reading. Pins 1 and 3 are wired to the supply rails given the device access to a 5 V reference range which fits within the 2.7-5.5 V range specified in the datasheet. Wire your prototype as shown to the right.
Task. Sensors are typically monitored for their data on a scheduled basis. Since the goals of any microcontroller-based embedded system should be efficiency and optimization, we'll employ an interrupt-based approach tht will have our code retrieve the TMP36's temperature reading at periodic intervals. In the code below we'll take 10 readings at consecutive 2 s intervals.
// PROJECT :TMP36Test
// PURPOSE :Interval monitoring of an Analog (Voltage-sensitive) TMP36 Temperature Sensor
// COURSE :TEJ3M
// AUTHOR :C. D'Arcy
// DATE :2025 11 28
// MCU :*
// STATUS :Working
// REFERENCE:http://darcy.rsgc.on.ca/ACES/Datasheets/TMP35_36_37.pdf
// REFERENCE:UTF-8 Character Set: https://www.utf8-chartable.de/
// TUTORIAL :https://learn.adafruit.com/tmp36-temperature-sensor
#include <TimerOne.h> //Timer1 library for interrupt-scheduled monitoring for TMP36 sensor
#define INTERVAL 1000000 //period (us) between readings
#define OFFSET -53 //environmentally-compensated temperature offset (adjust to DMM)
#define TMP36 A5 //TMP36 Pin 2. Supply pins (1-VCC, 3-GND) are in the rails
#define NUMSAMPLES 5 //Number of samples to obtain before stopping
float vRef = 5.0; // define the voltage reference (2.7V <-> 5.0V)
uint16_t rawADC; // the raw 10-bit ADC reading
float tempC; // the (converted) temperature in degrees Celsius
volatile boolean triggered = false; //set by the ISR to trigger a sampling
uint16_t count = 0; //monitor the number of samples taken
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //establish the baud rate for communication
while (!Serial) {} //wait for acknowledgement...
Timer1.initialize(INTERVAL); //set period between sampling
Timer1.attachInterrupt(ISR_Capture); //Interrupt Service Routine for scheduled reads
}
//Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) to request sampling of the TMP36 sensor
//Note: do as little as possible to avoid interrupting an interrupt
void ISR_Capture() {
triggered = true;
}
void loop() {
if (triggered) { //a sampling has been requested
triggered = false; //first things first: prepare for next interrupt
count++; //one more sample taken
rawADC = analogRead(TMP36); // Obtain next reading
//Since the TMP36 is linearly correlated a map function will suffice for the conversion
tempC = map(rawADC, 0, 1023, OFFSET, 125);
//publish the results
Serial.print("raw ADC (0-1023): " + String(rawADC) + "\tCelsius: ");
tempC = map(rawADC, 0, 1024, 0, vRef * 1000) / 10.0 + OFFSET;
Serial.print(tempC);
Serial.write(0xC2); //the degree symbol for improved appearance
Serial.write(0xB0); //See reference above
Serial.println('C');
}
if (count == NUMSAMPLES) {
Serial.println("End of Monitoring"); //hold
while (1) {}
}
}
2. Logging Sensor Data in Nano's Onboard EEPROM
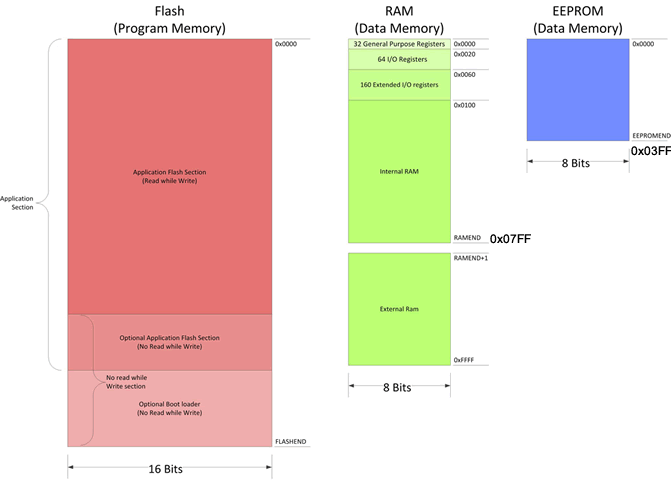 The AVR ATmega328p has 1 KB of onboard non-volatile memory referred to as Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPPROM). This is the blue memory in the graphc to the right. EEPROM is byte-oriented with an address space of [0,1023]. This is an ideal storage vehicle for persisent data such lookup tables (LUTs) such as conversion tables and font maps. Although it can be used for logging sensor data such as in our the example below, caution must be exercised as it is relatively slow and it has a limited number of read/write cycles (100,000).
The AVR ATmega328p has 1 KB of onboard non-volatile memory referred to as Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPPROM). This is the blue memory in the graphc to the right. EEPROM is byte-oriented with an address space of [0,1023]. This is an ideal storage vehicle for persisent data such lookup tables (LUTs) such as conversion tables and font maps. Although it can be used for logging sensor data such as in our the example below, caution must be exercised as it is relatively slow and it has a limited number of read/write cycles (100,000).
Given that this is your first introduction to exploiting EEPROM's capabilities, we'll restrict ourselves to the EEPROM.h library that is built into the Arduino toolchain. It is recommended that you explore the EEPROM library examples provided with the Arduino IDE (File>Examples>EEPROM.h) for deeper coverage.
Note that the EEPROM Library's read() and write() functions are byte oriented so care must by taken when storing and retrieving multi-byte data values of types such as uint16_t, float or structs.
Task. Using the same prototype as in the previous task, develop a sketch for the Nano that obtains and stores 5 temperature readings, 1 per second, from the TMP36 and stores each, as floats, into EEPROM. When all the samples have been logged, read them back from EEPROM for confirmation.
// PROJECT :TMP36TestEEPROM
// PURPOSE :Followup for TMP36Test. Storage and retrieval of (float) TMP36 data to/from Nano's EEPROM.
// COURSE :TEJ3M
// AUTHOR :C. D'Arcy
// DATE :2025 11 28
// MCU :*
// STATUS :Working
// REFERENCE:http://darcy.rsgc.on.ca/ACES/Datasheets/TMP35_36_37.pdf
// REFERENCE:UTF-8 Character Set: https://www.utf8-chartable.de/
// TUTORIAL :https://learn.adafruit.com/tmp36-temperature-sensor
#include <EEPROM.h> //functional access to ATmega328p's EEPROM
#include <TimerOne.h> //Timer1 library for interrupt-scheduled monitoring for TMP36 sensor
#define INTERVAL 1000000 //period (us) between readings
#define OFFSET -53 //environmentally-compensated temperature offset (adjust to DMM)
#define TMP36 A5 //TMP36 Pin 2. Supply pins (1-VCC, 3-GND) are in the rails
#define NUMSAMPLES 5 //Number of samples to obtain before stopping
#define SETTLE 20 //EEPROM access takes time. Allow EEPROM I/O operations time to complete
float vRef = 5.0; // define the voltage reference (2.7V <-> 5.0V)
uint16_t rawADC; // the raw 10-bit ADC reading
float tempC; // the (converted) temperature in degrees Celsius
volatile boolean triggered = false; //set by the ISR to trigger a sampling
uint16_t count = 0; //monitor the number of samples taken
uint16_t address; //support for EEPROM addresses
uint8_t sizeofData = sizeof(float); //how many bytes for each float value? (4)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //establish the baud rate for communication
while (!Serial) {} //wait for acknowledgement...
Timer1.initialize(INTERVAL); //set period between sampling
Timer1.attachInterrupt(ISR_Capture); //Interrupt Service Routine for scheduled reads
}
//Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) to request sampling of the TMP36 sensor
//Note: do as little as possible to avoid interrupting an interrupt
void ISR_Capture() {
triggered = true;
}
void loop() {
if (triggered) { //a sampling has been requested
triggered = false; //first things first: prepare for next interrupt
rawADC = analogRead(TMP36); // Obtain next reading
//Since the TMP36 is linearly correlated a map function will suffice for the conversion
tempC = map(rawADC, 0, 1023, OFFSET, 125);
Serial.print("raw ADC (0-1023): " + String(rawADC) + "\tCelsius: ");
float tempC = map(rawADC, 0, 1024, 0, vRef * 1000) / 10.0 + OFFSET;
//store the float reading in EEPROM
address = count * sizeofData;
EEPROM.put(address, tempC);
delay(SETTLE);
Serial.print(tempC);
Serial.write(0xC2); //the degree symbol for improved appearance
Serial.write(0xB0); //See reference above
Serial.println("C\tStored at EEPROM Address: " + String(address));
count++; //one more sample taken
}
//Once all the samples have been secured in EEPROM, confirm them by reading them back
if (count == NUMSAMPLES) {
Serial.println("End of Monitoring");
for (uint16_t address = 0; address < NUMSAMPLES * sizeofData; address += sizeofData) {
Serial.print("Reading from EEPROM Address: " + String(address) + "\t");
EEPROM.get(address, tempC);
delay(SETTLE);
Serial.print(tempC);
Serial.write(0xC2); //the degree symbol for improved appearance
Serial.write(0xB0); //See reference above
Serial.println('C');
}
while (1) {}
}
}
3. EEPROM: ASCII Lookup Table
As mentioned earlier, most digital EEPROM storage assets have a limited read/write threshold of approximately 100,000 cycle. As such it is perhaps best suited as a semi-permanent storage device for data in a lookup table (LUT). One such table could be the matrix data for each of the ASCII characters to be displayed on an 8×8 (mini) matrix.
Consider this. The 7-bit ASCII table defines 128 characters. Since each character requires 8 bytes (rows) to fill the matrix, it would need 1024 bytes in total to define the table. This happens to be exactly the number of bytes available in the ATmega328p's EEPROM!
Try it Yourself
1. The first of two sketches offered below loads character data for an 8×8 matrix font into the Nano's EEPROM. For example, since the ASCII value for 'A' is 65, the 8 rows defining the character are loaded at address 65×8 or 520. This makes retrieval of the row data for any particular character straightforward. Run this sketch first to flash EEPPROM with this lookup table.
2. The second sketch expects that EPPROM is loaded with the character matrix table in order to access and present each character in the message, one at a time, at a pace defined by the Timer1 Interrupt.
Load EEPROM with ASCII Lookup Table
// Purpose :Writes ASCII Character Map to EEPROM
// Reference:http://arduino-er.blogspot.ca/2014/08/port-ascii-font-to-arduino-88-led-matrix.html
// Author :C. D'Arcy
// Date :2018 01 24
// Status :Working
#include <EEPROM.h>
uint16_t address = 0;
uint8_t font[128][8] = {
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0000 (nul)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0001
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0002
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0003
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0004
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0005
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0006
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0007
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0008
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0009
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+000A
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+000B
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+000C
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+000D
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+000E
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+000F
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0010
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0011
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0012
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0013
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0014
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0015
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0016
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0017
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0018
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0019
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+001A
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+001B
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+001C
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+001D
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+001E
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+001F
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0020 (space)
{ 0x18, 0x3C, 0x3C, 0x18, 0x18, 0x00, 0x18, 0x00}, // U+0021 (!)
{ 0x36, 0x36, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0022 (")
{ 0x36, 0x36, 0x7F, 0x36, 0x7F, 0x36, 0x36, 0x00}, // U+0023 (#)
{ 0x0C, 0x3E, 0x03, 0x1E, 0x30, 0x1F, 0x0C, 0x00}, // U+0024 ($)
{ 0x00, 0x63, 0x33, 0x18, 0x0C, 0x66, 0x63, 0x00}, // U+0025 (%)
{ 0x1C, 0x36, 0x1C, 0x6E, 0x3B, 0x33, 0x6E, 0x00}, // U+0026 (&)
{ 0x06, 0x06, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0027 (')
{ 0x18, 0x0C, 0x06, 0x06, 0x06, 0x0C, 0x18, 0x00}, // U+0028 (()
{ 0x06, 0x0C, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x0C, 0x06, 0x00}, // U+0029 ())
{ 0x00, 0x66, 0x3C, 0xFF, 0x3C, 0x66, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+002A (*)
{ 0x00, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x3F, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+002B (+)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x06}, // U+002C (,)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x3F, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+002D (-)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x00}, // U+002E (.)
{ 0x60, 0x30, 0x18, 0x0C, 0x06, 0x03, 0x01, 0x00}, // U+002F (/)
{ 0x3E, 0x63, 0x73, 0x7B, 0x6F, 0x67, 0x3E, 0x00}, // U+0030 (0)
{ 0x0C, 0x0E, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x3F, 0x00}, // U+0031 (1)
{ 0x1E, 0x33, 0x30, 0x1C, 0x06, 0x33, 0x3F, 0x00}, // U+0032 (2)
{ 0x1E, 0x33, 0x30, 0x1C, 0x30, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0033 (3)
{ 0x38, 0x3C, 0x36, 0x33, 0x7F, 0x30, 0x78, 0x00}, // U+0034 (4)
{ 0x3F, 0x03, 0x1F, 0x30, 0x30, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0035 (5)
{ 0x1C, 0x06, 0x03, 0x1F, 0x33, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0036 (6)
{ 0x3F, 0x33, 0x30, 0x18, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x00}, // U+0037 (7)
{ 0x1E, 0x33, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x33, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0038 (8)
{ 0x1E, 0x33, 0x33, 0x3E, 0x30, 0x18, 0x0E, 0x00}, // U+0039 (9)
{ 0x00, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x00}, // U+003A (:)
{ 0x00, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x06}, // U+003B (//)
{ 0x18, 0x0C, 0x06, 0x03, 0x06, 0x0C, 0x18, 0x00}, // U+003C (<)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x3F, 0x00, 0x00, 0x3F, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+003D (=)
{ 0x06, 0x0C, 0x18, 0x30, 0x18, 0x0C, 0x06, 0x00}, // U+003E (>)
{ 0x1E, 0x33, 0x30, 0x18, 0x0C, 0x00, 0x0C, 0x00}, // U+003F (?)
{ 0x3E, 0x63, 0x7B, 0x7B, 0x7B, 0x03, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0040 (@)
{ 0x0C, 0x1E, 0x33, 0x33, 0x3F, 0x33, 0x33, 0x00}, // U+0041 (A)
{ 0x3F, 0x66, 0x66, 0x3E, 0x66, 0x66, 0x3F, 0x00}, // U+0042 (B)
{ 0x3C, 0x66, 0x03, 0x03, 0x03, 0x66, 0x3C, 0x00}, // U+0043 (C)
{ 0x1F, 0x36, 0x66, 0x66, 0x66, 0x36, 0x1F, 0x00}, // U+0044 (D)
{ 0x7F, 0x46, 0x16, 0x1E, 0x16, 0x46, 0x7F, 0x00}, // U+0045 (E)
{ 0x7F, 0x46, 0x16, 0x1E, 0x16, 0x06, 0x0F, 0x00}, // U+0046 (F)
{ 0x3C, 0x66, 0x03, 0x03, 0x73, 0x66, 0x7C, 0x00}, // U+0047 (G)
{ 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x3F, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x00}, // U+0048 (H)
{ 0x1E, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0049 (I)
{ 0x78, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x33, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+004A (J)
{ 0x67, 0x66, 0x36, 0x1E, 0x36, 0x66, 0x67, 0x00}, // U+004B (K)
{ 0x0F, 0x06, 0x06, 0x06, 0x46, 0x66, 0x7F, 0x00}, // U+004C (L)
{ 0x63, 0x77, 0x7F, 0x7F, 0x6B, 0x63, 0x63, 0x00}, // U+004D (M)
{ 0x63, 0x67, 0x6F, 0x7B, 0x73, 0x63, 0x63, 0x00}, // U+004E (N)
{ 0x1C, 0x36, 0x63, 0x63, 0x63, 0x36, 0x1C, 0x00}, // U+004F (O)
{ 0x3F, 0x66, 0x66, 0x3E, 0x06, 0x06, 0x0F, 0x00}, // U+0050 (P)
{ 0x1E, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x3B, 0x1E, 0x38, 0x00}, // U+0051 (Q)
{ 0x3F, 0x66, 0x66, 0x3E, 0x36, 0x66, 0x67, 0x00}, // U+0052 (R)
{ 0x1E, 0x33, 0x07, 0x0E, 0x38, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0053 (S)
{ 0x3F, 0x2D, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0054 (T)
{ 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x3F, 0x00}, // U+0055 (U)
{ 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x0C, 0x00}, // U+0056 (V)
{ 0x63, 0x63, 0x63, 0x6B, 0x7F, 0x77, 0x63, 0x00}, // U+0057 (W)
{ 0x63, 0x63, 0x36, 0x1C, 0x1C, 0x36, 0x63, 0x00}, // U+0058 (X)
{ 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0059 (Y)
{ 0x7F, 0x63, 0x31, 0x18, 0x4C, 0x66, 0x7F, 0x00}, // U+005A (Z)
{ 0x1E, 0x06, 0x06, 0x06, 0x06, 0x06, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+005B ([)
{ 0x03, 0x06, 0x0C, 0x18, 0x30, 0x60, 0x40, 0x00}, // U+005C (\)
{ 0x1E, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+005D (])
{ 0x08, 0x1C, 0x36, 0x63, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+005E (^)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xFF}, // U+005F (_)
{ 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x18, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+0060 (`)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x1E, 0x30, 0x3E, 0x33, 0x6E, 0x00}, // U+0061 (a)
{ 0x07, 0x06, 0x06, 0x3E, 0x66, 0x66, 0x3B, 0x00}, // U+0062 (b)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x1E, 0x33, 0x03, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0063 (c)
{ 0x38, 0x30, 0x30, 0x3e, 0x33, 0x33, 0x6E, 0x00}, // U+0064 (d)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x1E, 0x33, 0x3f, 0x03, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0065 (e)
{ 0x1C, 0x36, 0x06, 0x0f, 0x06, 0x06, 0x0F, 0x00}, // U+0066 (f)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x6E, 0x33, 0x33, 0x3E, 0x30, 0x1F}, // U+0067 (g)
{ 0x07, 0x06, 0x36, 0x6E, 0x66, 0x66, 0x67, 0x00}, // U+0068 (h)
{ 0x0C, 0x00, 0x0E, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+0069 (i)
{ 0x30, 0x00, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x33, 0x33, 0x1E}, // U+006A (j)
{ 0x07, 0x06, 0x66, 0x36, 0x1E, 0x36, 0x67, 0x00}, // U+006B (k)
{ 0x0E, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+006C (l)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x33, 0x7F, 0x7F, 0x6B, 0x63, 0x00}, // U+006D (m)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x1F, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x00}, // U+006E (n)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x1E, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x00}, // U+006F (o)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x3B, 0x66, 0x66, 0x3E, 0x06, 0x0F}, // U+0070 (p)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x6E, 0x33, 0x33, 0x3E, 0x30, 0x78}, // U+0071 (q)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x3B, 0x6E, 0x66, 0x06, 0x0F, 0x00}, // U+0072 (r)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x3E, 0x03, 0x1E, 0x30, 0x1F, 0x00}, // U+0073 (s)
{ 0x08, 0x0C, 0x3E, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x2C, 0x18, 0x00}, // U+0074 (t)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x6E, 0x00}, // U+0075 (u)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x1E, 0x0C, 0x00}, // U+0076 (v)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x63, 0x6B, 0x7F, 0x7F, 0x36, 0x00}, // U+0077 (w)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x63, 0x36, 0x1C, 0x36, 0x63, 0x00}, // U+0078 (x)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x33, 0x33, 0x33, 0x3E, 0x30, 0x1F}, // U+0079 (y)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x3F, 0x19, 0x0C, 0x26, 0x3F, 0x00}, // U+007A (z)
{ 0x38, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x07, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x38, 0x00}, // U+007B ({)
{ 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x00, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x00}, // U+007C (|)
{ 0x07, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x38, 0x0C, 0x0C, 0x07, 0x00}, // U+007D (})
{ 0x6E, 0x3B, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, // U+007E (~)
{ 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00} // U+007F
};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// for (uint8_t row = 32; row < 96; row++) { //this is for the ATiny84 (512KB EEPROM)
for (uint8_t row = 0; row < 128; row++) {
if (row >= ' ') {
Serial.println("Writing Character: " + String(row));
}
for (uint8_t col = 0; col < 8; col++) {
EEPROM.write(address++, font[row][col]);
delayMicroseconds(5);
}
}
Serial.println("Done");
address = 'A'<<3;
Serial.println(address);
Serial.println('A'+'B');
Serial.println(String("A")+String("B"));
Serial.println(EEPROM.read(address), HEX);
}
void loop() {
}
Display a message (msg[]) on your MatrixMadeEZ
// PROJECT :MatrixMadeEZASCIIFromEEPROM
// PURPOSE :Demo program of the MatrixMadeEZ Device (original design by H. Reed)
// RESULT :ASCII Characters of the message are displayed at a speed governed by Timer1 Interrupt
// AUTHOR :C. D'Arcy.
// DATE :Created: 2022 12 13. Confirmed: 2025 11 28.
// uC :328P (Nano)
// STATUS :Working. Partially commented.
// REFERENCE:https://cdn-shop.adafruit.com/datasheets/1079datasheet.pdf
// :https://www.pjrc.com/teensy/td_libs_TimerOne.html
// Library provides access to 328P's Timer 1 services...
#include <TimerOne.h>
#include <EEPROM.h>
// COMPILER PREPROCESSORS
#define POTSPEEDVCC A0 //software supply
#define POTSPEEDIN A1 //
#define POTSPEEDGND A2 //software supply
#define POTDIMIN A5 //hardware supply
#define DIMMING 0 //0:bright, 250ish:dim
#define PACE 0 //0:as fast as possible, 50:to observe scanning
#define MMEZDIM 3 //to /G on TPIC (PWM)
#define MMEZDATA 9 //
#define MMEZCLOCK 8 //
#define MMEZLATCH 7 //
#define LIMIT 8 //adjust for numbers of rows (length of main diagonal) (1-8)
#define INTERVAL 1000000 //Interval between TimerOne interrupts (in uS)...
uint8_t row = 0; //to scan the main diagonal...
uint8_t colData; //...equate the row and column coordinates
char msg[] = "RSGC ACES"; //play an array of characters...
volatile uint8_t msgLength = sizeof(msg) - 1; //determine the length of the message....
volatile uint8_t index = 0; //start t the first character...
void setup() {
pinMode(POTSPEEDVCC, OUTPUT);
pinMode(POTSPEEDGND, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(POTSPEEDVCC, HIGH);
digitalWrite(POTSPEEDGND, LOW);
pinMode(MMEZDIM, OUTPUT); //
pinMode(MMEZDATA, OUTPUT); //
pinMode(MMEZCLOCK, OUTPUT); //
pinMode(MMEZLATCH, OUTPUT); //
analogWrite(MMEZDIM, DIMMING); //default: no dimming (full brightness)
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {}
Timer1.initialize(INTERVAL); //establish the interrupt period
Timer1.attachInterrupt(ISR_Alternate); //ISR to be called on every Timer1 Overflow
}
//Switch between glyphs (rows) of the matrix
void ISR_Alternate() {
if (index == msgLength - 1)
index = 0;
else
index++;
}
void loop() {
colData = EEPROM.read((msg[index] << 3) + row); //(font[msg[index]][row]; //1 << row;
shiftOut(MMEZDATA, MMEZCLOCK, LSBFIRST, colData); //Column data first: note the shift order
shiftOut(MMEZDATA, MMEZCLOCK, LSBFIRST, 1 << row); //and then the (TPIC) row data
digitalWrite(MMEZLATCH, LOW); //create a rising edge on latch pin
digitalWrite(MMEZLATCH, HIGH); //
row++; //advance the row...
if (row == LIMIT) row = 0; //are we done? If so, start again
delay(PACE); //control the display speed of the scanning
// DISPLAY SPEED AND DIMMING...
/*
uint16_t adcReading = analogRead(POTSPEEDIN); // comment ADC influences in or out as required.
// Serial.print("SPEED: "); // activating Serial comm slows PoV down
// Serial.println(adcReading);
delay(adcReading);
adcReading = analogRead(POTDIMIN);
analogWrite(MMEZDIM, adcReading);
// Serial.print("\tDIM: ");
// Serial.println(adcReading);
*/
}